This article helps in explaining how to change the style of an UI element like Button, TextView etc. in an android application and different ways in which you can change the styling of different UI elements in your android application. Moreover, this post helps you in understanding the method of creating your own custom styles and how to use custom styles in an android application.
Styling your android application definitely helps in making your android app more attractive and interactive. By default, an android system provides a number of styling options for each UI element e.g. you can change the background colour, text colour, width, height and so many other properties of various UI elements like Buttons, TextView etc. There are a number of ways in which you can play with the styling of your android app or even individual elements present in your android app. Let’s take a brief look at all of them.
Let’s understand the above xml code in detail –
Now that we’ve created our custom style we need to tell the android system to use this style for a particular UI Element. To do this, go to your layout file and right click on the UI element whose style you want to set to this custom style i.e. “mystyle”. Now go to “Show In” -> “Properties”. This will open the Properties View. Scroll down to “style” and set its value to your custom style (i.e. the name attribute of style tag that I mentioned before and in this case it's "mystyle").
Styling your android application definitely helps in making your android app more attractive and interactive. By default, an android system provides a number of styling options for each UI element e.g. you can change the background colour, text colour, width, height and so many other properties of various UI elements like Buttons, TextView etc. There are a number of ways in which you can play with the styling of your android app or even individual elements present in your android app. Let’s take a brief look at all of them.
Different Ways of Changing Style of UI Element in Android App -
- Styling each UI element separately –
This is the basic method in which you set the styling of
each UI element separately using the Property View in eclipse. To set the style
using this process all you have to do is to follow these steps –
- Right click on the UI element for which you have to set the style.
- Now go to “Show In” -> “Properties”. This will open the Properties View.
- In this property view you’ll be able to see a bunch of styling options for that UI element that you can change to modify the style of that UI element.
E.g. You can set the
text color to say green by scrolling down to “text color” property and setting
its value to #00FF00 or width to say 30dp etc.
While this method is all good and simple yet its use should
be avoided when you have a big app with lots of UI elements having the same
style. This is obvious as this method requires you to set styling of individual UI
elements separately. So, this method shouldn’t be used when you have many UI
elements for which you want the same styling.
- Creating Custom Styles –
What if your app has say 10
buttons and all of height 30dp, text color red and background color green. So in this
case setting up the styling values for each button separately would be time
consuming and inefficient. For this case it would be better to have a single
style and reuse that style whenever and wherever required, wouldn't it? In android this thing can be achieved by creating your own custom styles and use them as and when you require.To create your custom styles, the steps are as follows –
- First create a new XML file say style.xml and select its Resource Type to Values. This will create a style.xml file inside the res -> values folder in your project hierarchy. Take a look at the snap below.
- Open this style.xml file and go to the xml editor in eclipse. Although you can use the graphic editor but it’s better to make changes in the xml part by yourself.
- Now it’s time to edit the style.xml file. So, to make every button of height 30dp, text color red and background color green you’ll have to add the following lines in you style.xml file.
<style
name="mystyle" parent="@android:style/ButtonBar">
<item name="android:background">#00FF00</item>
<item name="android:textColor">#FF0000</item>
<item name="android:height">50dp</item>
</style>
Let’s understand the above xml code in detail –
- The first element is a style tag telling the android system that this is a custom style and the values contained in this file are specifying the style of a particular (or a group) of UI elements.
- Inside the style tag there’s an attribute “name”. This is used as a reference to this style. So if you want an UI element to use this style all you need to do is to set the style for that element to “mystyle” i.e. your custom style. Take a look at the snap below to see how to do this.
- There’s another attribute of style tag namely “parent”. By specifying a parent of a custom style, we are telling that this custom style should inherit all the default styling from the parent and then we can override the styling of certain properties as we need. It’s like inheritance, the base class – sub class relation.
- Now we need to override certain styling properties (or items) that we want different. For this create an item tag between the style opening and closing tags as shown above. In the “name” attribute of item tag you need to specify which property of an UI element you want to set. E.g. “android:background” should be used to set the background color and “android:textColor” is used for changing the text color.
Tip: Don’t worry about how to find these values like different values for the “parent” attribute or item’s name. Just use eclipse’s auto suggestions (start typing and press ctrl + space).
Now that we’ve created our custom style we need to tell the android system to use this style for a particular UI Element. To do this, go to your layout file and right click on the UI element whose style you want to set to this custom style i.e. “mystyle”. Now go to “Show In” -> “Properties”. This will open the Properties View. Scroll down to “style” and set its value to your custom style (i.e. the name attribute of style tag that I mentioned before and in this case it's "mystyle").
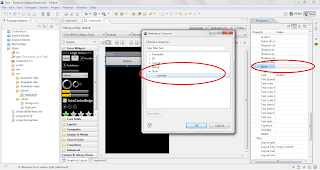 |
| How to Link a Custom Style to an UI Element. |
- Using an existing custom style to create a new custom style –
You can also use a
custom style to create another custom style. E.g. suppose you want a couple of
buttons in your app to have a white background but the rest of the properties
same as your custom style “mystyle” in style.xml that we created before. For
this all you have to do is to create another style element in your style.xml (below
you first style tag “mystyle”) and make the override for the properties you
want to change. So to make changes in the background property you have to make changes
like this –
<style
name="mystyle.bgwhite">
<item name="android:background">#FFFFFF</item>
</style>
Notice the name of
this style is “mystyle.bgwhite”.
Here “mystyle” is telling the parent custom style for this new style. This
style can be referred to in the same way as we did before.





